
In a webcast announcement, University of Utah researchers David Carrier and Steven Naleway, along with recent graduate Ethan Beseris, were awarded the 2021 Ig Nobel Peace Prize for a study exploring whether beards may serve an evolutionary purpose to protect the jaw during a fistfight.

The lighthearted awards, presented by Marc Abrahams of the science humor magazine Annals of Improbable Research, are a counterpoint to the mainstream Nobel Prizes, which will be awarded in October. Ig Nobel Prizes, awarded since 1991, are intended to celebrate science that “first make people laugh, and then make them think.” The U study is among this year’s 10 awardees.
This is the U’s first Ig Nobel Prize, and the story was immediately picked up by the media across the globe including in The Guardian , the South China Morning News, and across the country, including The Washington Post.
“Usually they give the awards to out-of-the-box questions, and that’s an important part of what science is about,” says Carrier, an evolutionary biologist and professor in the School of Biological Sciences, who adds that he pondered at first whether it was an award he wanted to accept. “I’m quite happy at this point. There was trepidation at first, but now that’s gone.”
“I honestly think it’s pretty cool that we got selected as Ig Nobel Prize laureates,” says Naleway, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering. “I am a big believer in the fact that there’s a lot of value to research that’s approachable for people.”
“It’s an honor to be an Ig Nobel Laureate,” says Beseris, who conducted the study as part of his undergraduate thesis. “I’m grateful to their organization for recognizing less traditional branches of science and giving our work a larger platform to be heard. Radical questions test the boundaries of our field and I believe it’s important that they receive attention.”
Bearded pugilists
The study, published in April 2020 in Integrative Organismal Biology, continues a line of research that Carrier has been pursuing for years. Given that humans are the only primates who fight by punching, could there be other aspects of human anatomy that evolved in connection with fisticuffs?
That question is called the “pugilism hypothesis” and Carrier has explored how different features unique to us among primates (planted heels, proportions of face bones, ability to form a fist and upper arm strength in males) specialize humans, particularly males, for fighting by punching.
“And so the beard, which our study shows provides some protection to some of the most vulnerable parts of the face when people punch, is just one more piece of the series,” Carrier says.
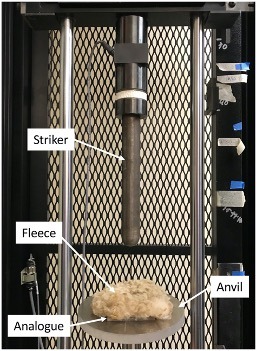
The researchers covered a fiber epoxy composite material similar to bone with sheep fleece, an analog for facial hair. They then dropped different weights onto the samples and found that samples with fleece absorbed 37% more energy than hairless samples and could withstand 16% more force before breaking.
Naleway’s involvement stems from his research in biomechanics and materials science. “If you talk to the researchers who do this kind of work, some of that biomechanics component is kind of missing,” he says, “and it can help us understand what’s going on, which obviously for this application of protection is incredibly important.”
Why does this matter from an evolutionary perspective?
“The beard covers the mandible, which is one of the primary targets,” Carrier says. “And when it breaks, without an orthopedic surgeon you’re in big trouble. If you broke a jaw 5,000 years ago, that was a life-threatening injury.”
Beseris says that studies of the pugilism hypothesis help us understand humans’ aggressive tendencies. “Evolution leaves clues in our anatomy that we can observe and document,” he says. “I believe these are the building blocks of how we address larger societal issues such as war, class disparity and racism.”
Notorious science
The work was previously awarded the 2020 Pineapple Science Prize in Physics, an analog to the Ig Nobel awards, presented in China by the Zhejiang Science Museum and science website Guokr.
Last year’s Ig Nobel awards included the diagnosis of misphonia, the distress at hearing other people chew, and the changes to the shape of an earthworm when it’s vibrated at high frequency.
This year the awards ceremony includes presentations of awards by “genuinely bemused genuine” Nobel laureates, an original mini-opera, very brief lectures on topics from drinking coffee to baby-washing technology and, according to the ceremony website, lots of paper airplanes.
Read more about past awards here.
by Paul Gabrielsen
This article originally appeared in @TheU.
